Introduction to Components
What is a Component?
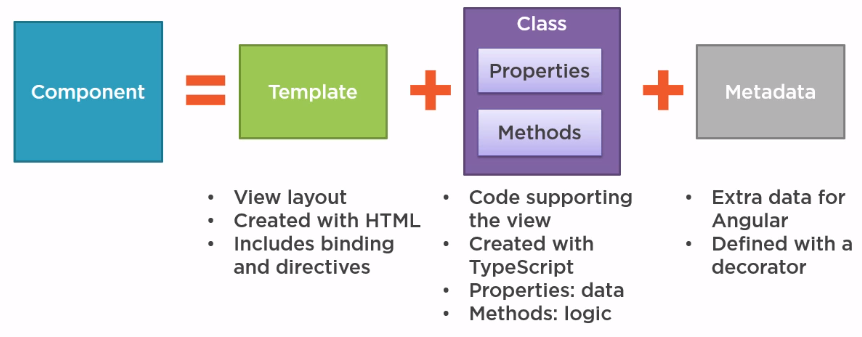
Creating the Component Class
Naming Suffix: Component
Root Module: AppComponent
Defining attributes (camelCase), datatypes and default values
export class AppComponent {
pageTitle: string = "Hola";
}
Defining the Metadata with a Decorator
Decorator: a function that adds metadata to a class, its members, its members attributes.
Prefixed with an @
Angular built-in decorators:
@Component()
@Component({
selector: 'pm-root',
template: `
<div><h1> {{pageTitle}} </h1>
<div>Primer Component</div>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
pageTitle: string = "Hola g";
}
Importing What We Need
It is a ES 2015
importstatement
Import from a third-party library, our own ES modules or from Angular.
Angular is modular (https://www.npmjs.com/~angular\:
- @angular/core
- @angular/animate
- @angular/http
- @angular/router
Boostrapping the Angular Application
Telling Angular to load our root component is called Boostrapping.
Define host application: index.html (with a directive - custom element - used as selector)
Define root Angular component.
Single Page Application is called to the Angular application (because only one host page).
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Acme Product Management</title>
<base href="/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
</head>
<body>
<pm-root></pm-root>
</body>
</html>
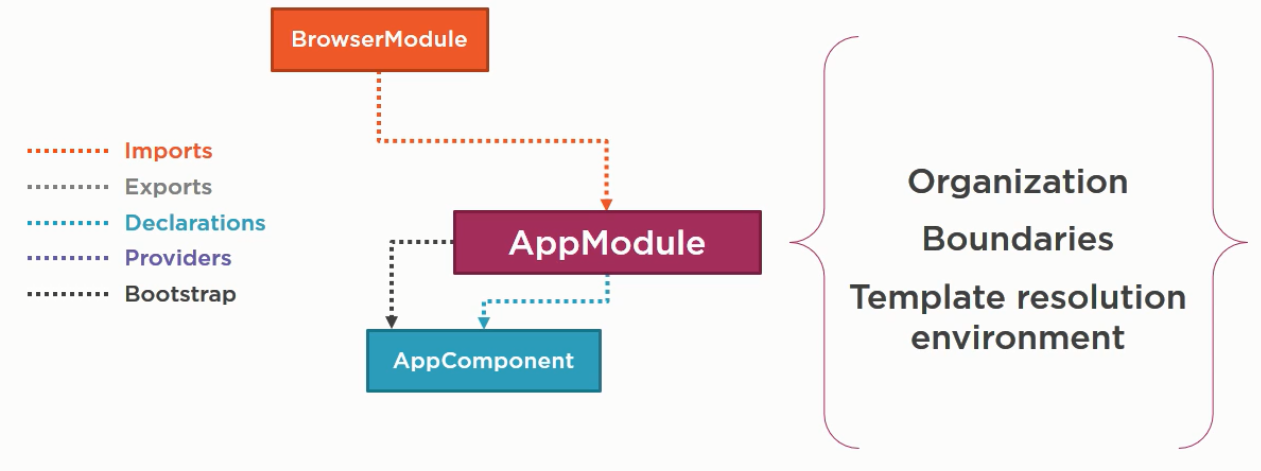
Defining Angular module
- Defined as a class
- Identify the class as an Angular module using @NgModule
- Declarations section: array of components which belong to this module
- Imports section: array of external modules (own, angular modules or third-party)
BrowserModule: it is a module every browser application must import. It is important to application service providers such as error handling- Bootstrap section: defines the startup component of the application . This startup must contain the selector used in the index.html
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
Checklist for Creating a Component
- Create a class which contains the code
- Use the decorator for the Metadata (for view template and HTML)
- Import any third party
- For convention the class name must be PascalCasing and posfixed by the word "Component"
- Use export keyword as part of the class declaration
- Data in properties
- Select and appropriate datatype when using Typescript and a default value
- Use camelCase for the property names
- Logical methods with camelCase
- Use @ for decorator
- HTML for template
- import keyword: followed by member name and module path both are case sensitive. Dont need to specify the extension
References
https://blogs.msmvps.com/deborahk/angular-2-getting-started-problem-solver/