Angular 2 Getting Started
https://app.pluralsight.com/library/courses/angular-2-getting-started-update/table-of-contents
Why Angular?
- Expressive HTML
- Powerful Data Binding
- Modular By Design
- Built-in Backend Integration
Why Angular and not AngularJS?
- Build for Speed (initial loads, change detection, rendering times)
- Modern (latest Javascript standards, classes, modules, decorators, support to Greenfield and Legacy browsers)
- Simplified API (fewer built-in directives, simpler bindings, less things to learn)
- Enhances productivity
Anatomy of Angular Application
An application is a composition of components and services which operate along them.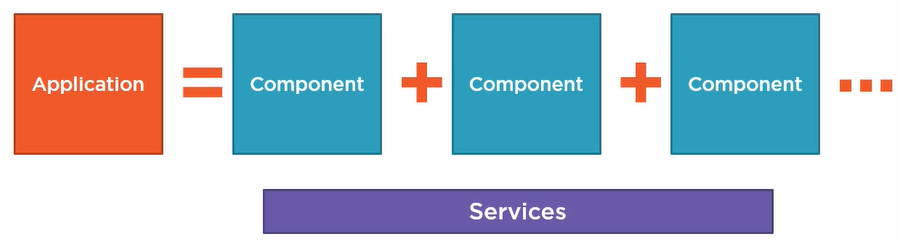
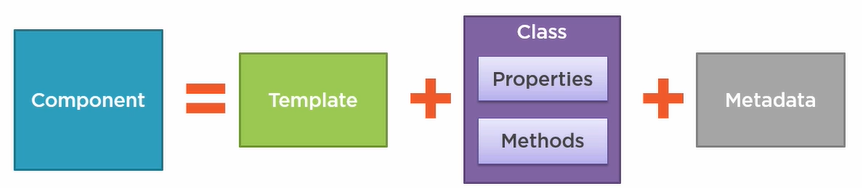
The component is conformed of these modules.
- Template: HTML fragment to define the view
- Class: Associated to the view, it contains methods and properties
- Metadata: Additional information to identify the class as an Angular component.
Now the form to organize and put all these components together is:
- Angular modules to organize application into cohesive blocks of functionality
- Every Angular application has at least one Angular module called application's root Angular module
- Every Angular application has one or more feature Angular modules focus on an specific application feature.
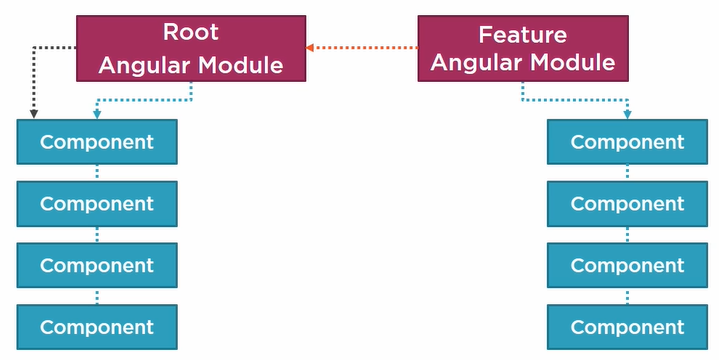
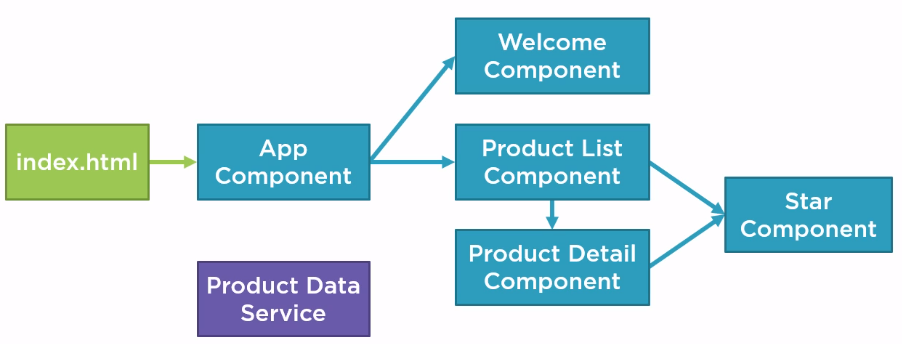
A sample Product Management application could be composed of the next components:
First Things to Do
Selecting Language
- Javascript Language Specification
- ECMAScript (ES)
- ES 3 (for old browsers)
- ES 5 (for most modern browsers, no compile require)
- ES 2015 o ES 6 (latest release but not many browsers support it yet, so the transpilers are in the rescue, compile require, new powerful features)
- Typescript
- Superset of Javascript
- String typing
- Great IDE tooling (inline documentation, syntax checking, code navigation, advanced refactorings)
- Typescript was used to build Angular 2
- Opensource
- Typescript type definition files (*.d.ts)
- Class-based object-orientation
- Dart
- Non Javascript
Selecting Editor
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- Support Typescript
- Runs in any OS
- https://code.visualstudio.com/
- WebStorm
- Atom
- Eclipse
- Sublime
- Others
Setting Up the Environment
- Installing npm 3 and later
- Node Package Manager
- Package Manager for Javascript
- Install libraries, applications and packages
- https://www.npmjs.com
- Setting Up Angular application
- Create an application folder
- Add package definitions and configuration files
- Install the packages
- Create the app's Angular module
- Create a main.ts file
- Create the host Web Page (index.hmtl)
- How?
- Using Angular quickstart (deprecated, instead use Angular CLI, only use for learning and prototyping): https://github.com/angular/quickstart
git clone https://github.com/angular/quickstart my-projnpm installnpm start- npm run build
- npm run build:w
- npm run serve
npm testnpm run e2e
- Using Angular CLI
- Generate components, modules, services, it scaffolds and executes unit and end-to-end tests, minimize, packages and prepare files for deployment.
- https://github.com/angular/angular-cli
ngcommand
- Using Angular quickstart (deprecated, instead use Angular CLI, only use for learning and prototyping): https://github.com/angular/quickstart
- Installing Angular Application
- Open in VisualStudioCode
- All files must be under src/ folder by convention
- Under /src folder must be the /app folder for files specific for the application
- Unser /app folder must be all feature folders which conform the application
- Must be all boilerplate files (configuration and setup files)
- Must be the package.json file for all dependencies. @angular entries are the Angular system libraries
Understanding Modules
- With Javascript
- Problems with namespaces made definitions in the global namespace
- Missing of code organization
- With AngularJS
- Appears Modules
With Typescript
- Also has Modules which are always out of the global namespace
- With ES 2015 it is a set of standards for defining Modules
- With ES 2015 a module is a file and a file is a module
- With ES 2015 is not necessary to define modules (it is implicit)
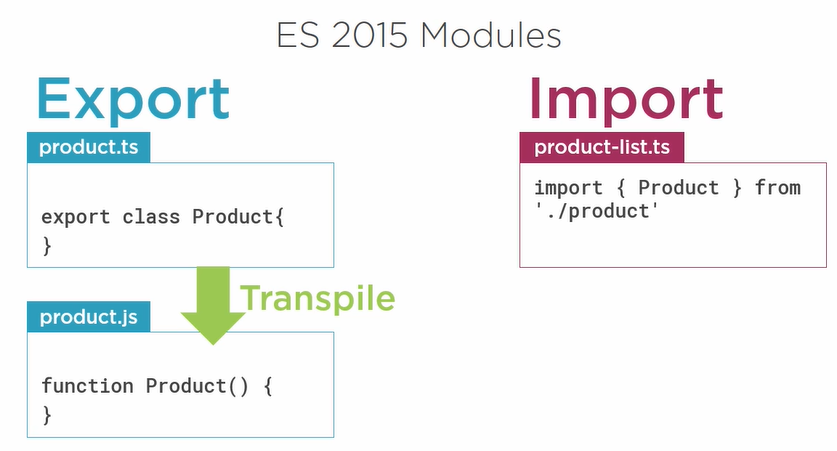
With Angular 5
- Angular modules help to organize code in cohesive blocks of functionality
- Each Angular application has a particular module called @module
- Define feature modules
- Define shared/common modules
- Allow loading on start or lazy load
- Each component declared into a module is specific for that module
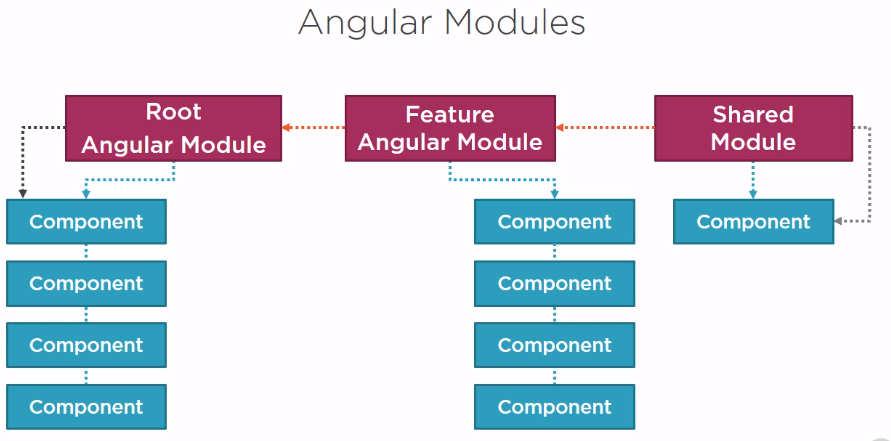
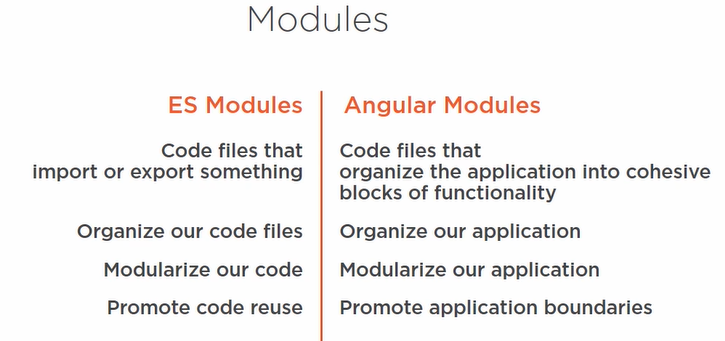
Difference between ES 2015 and Angular Modules
- Angular modules are application-based
- ES Modules are code-based