Vue.js Fundamentals
Contents
MVVM architecture paradigm
Declarative views
Defined properties, getters, setters
Reactivity and data binding
Dirty checking, DOM, and virtual DOM
Vue.js 1 and Vue.js 2
Reusable components
Plugins, directives, custom directives, custom plugins
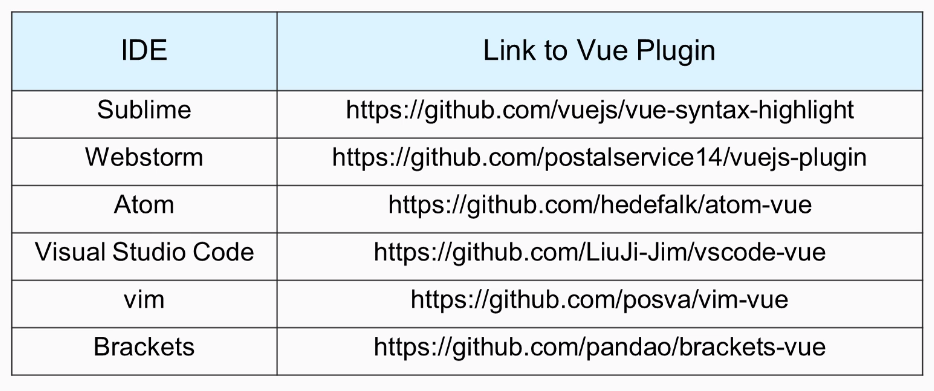
Debugging Vue.js application
MVVM architecture paradigm
First:
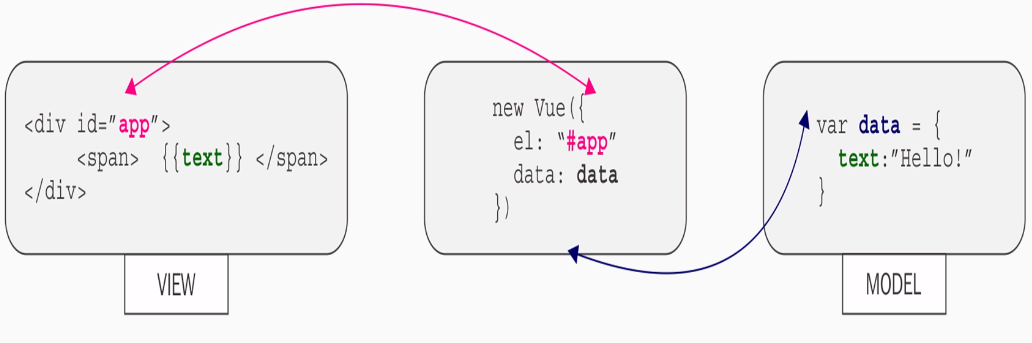
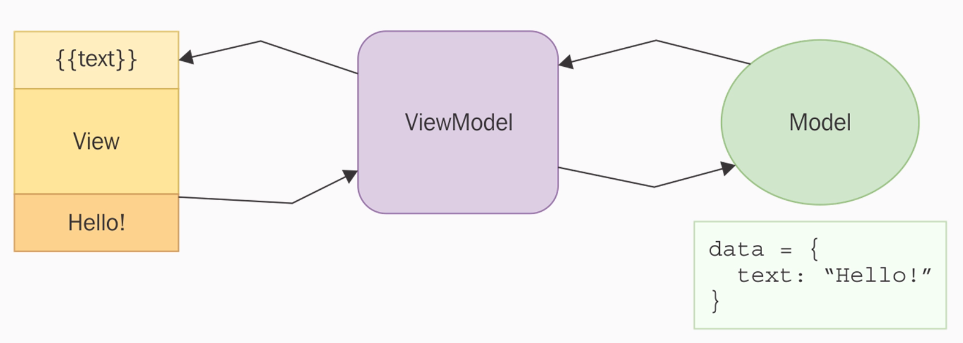
Second: ViewModel is in charge of two-way data binding.
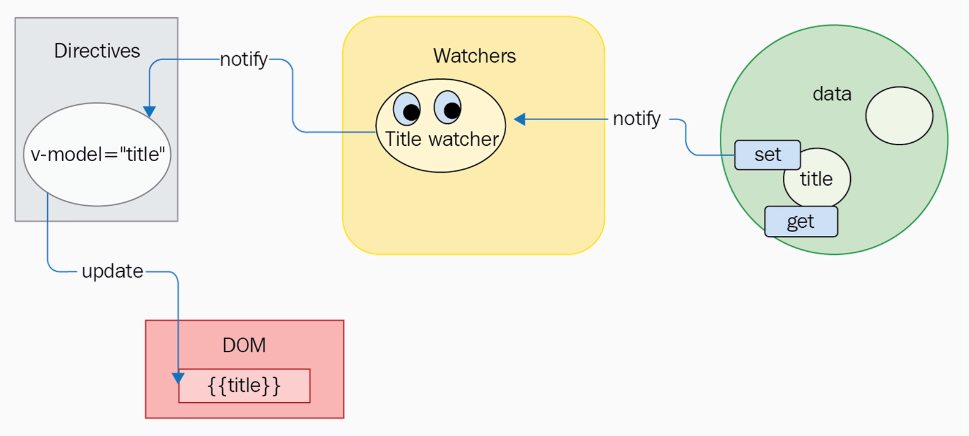
Defined properties, getters, setters
Internally, Vue.js uses Object.defineProperty().

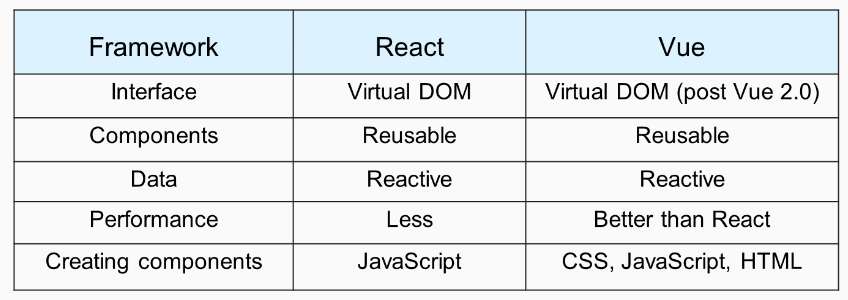
Comparing with other frameworks
React JS vs Vue.js
Strong: creating components in Vue.js is more flexible even with JSX, each section (JS, CSS and HTML) into their own tag. No learning of JSX and ES2015 syntax. In vue.js is allowed the <style scoped>.
Scope style: allows access to globally defined variables, enables creating or redefining styles.
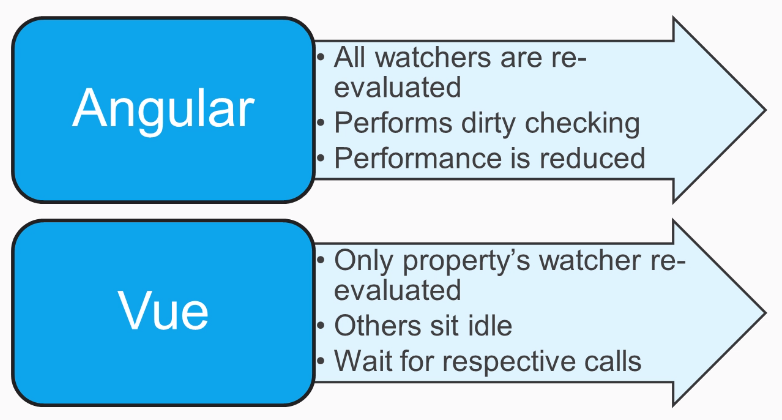
Angular and Angular 2 vs Vue.js
Angular 1
https://angular.io/guide/quickstart
Components, Plugins and Directives
Reusable components
Plugin, filters and mixins
Reusable components
Use and reuse as bricks. Own scope of styles and bindings
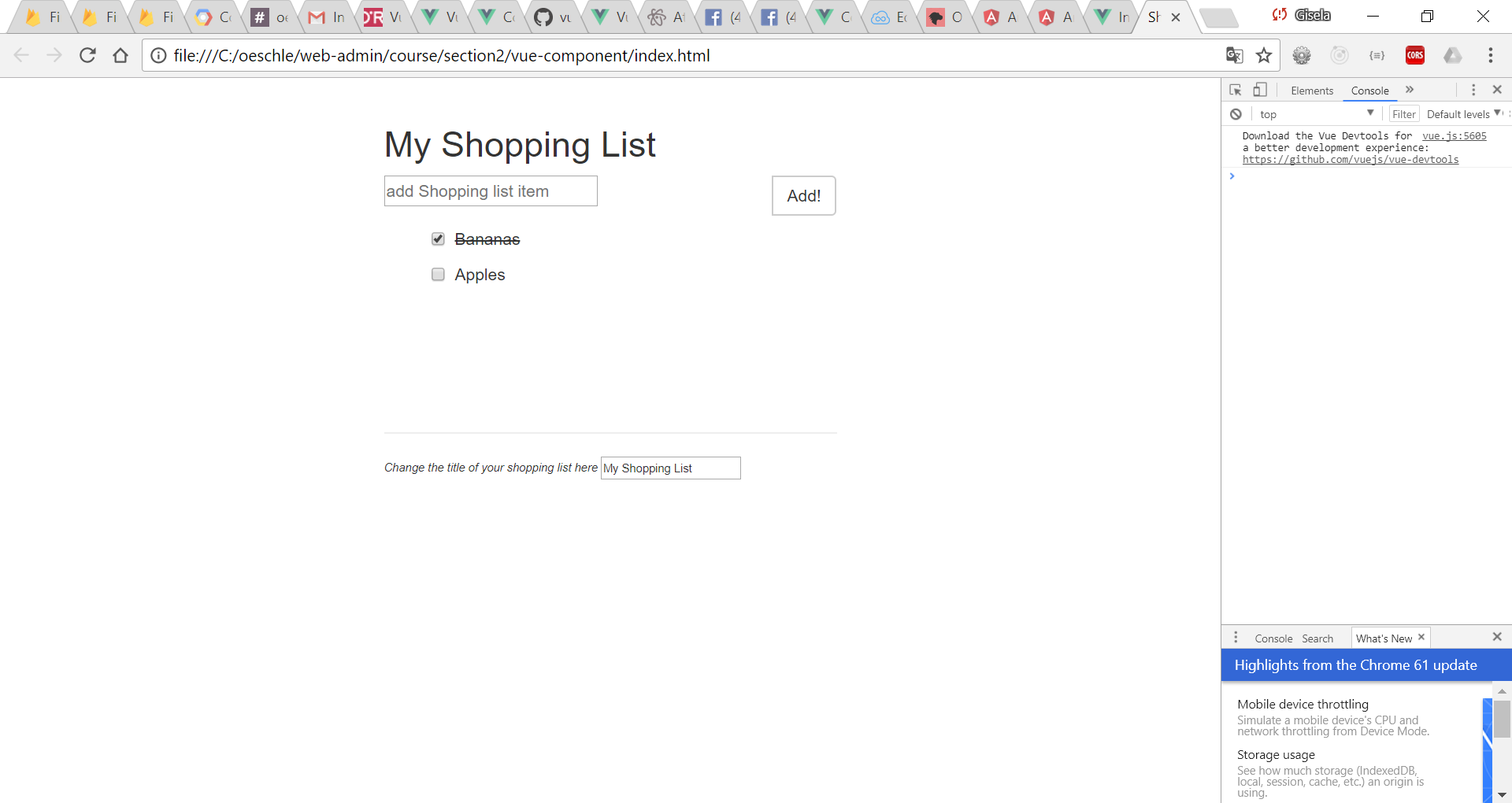
Example: index,html and script.js for simple Shopping List using only reusable components.
script.js file
var data = {
items: [{ text: 'Bananas', checked: true },
{ text: 'Apples', checked: false }],
title: 'My Shopping List',
newItem: ''
};
/**
* Declaring components
*/
var ItemsComponent = Vue.extend({
data: function() {
return data;
},
template: '<ul>' +
'<li v-for="item in items" :class="{ \'removed\' : item.checked }">' +
' <div class="checkbox">' +
' <label>' +
' <input type="checkbox" v-model="item.checked"> {{ item.text }}' +
' </label>' +
' </div>' +
'</li>' +
'</ul>'
});
var ChangeTitleComponent = Vue.extend({
data: function() {
return data;
},
template: '<input v-model="title" />'
});
var AddItemComponent = Vue.extend({
data: function() {
return data;
},
methods: {
addItem: function() {
var text;
text = this.newItem.trim();
if (text) {
this.items.push({
text: text,
checked: false
});
this.newItem = "";
}
}
},
template:
'<div class="input-group">' +
' <input v-model="newItem" @keyup.enter="addItem" placeholder="add Shopping list item" type="text" /> ' +
' <span class="input-group-btn">' +
' <button @click="addItem" class="btn btn-default" type="button">Add!</button>' +
' </span>' +
'</div>'
});
/**
* Registering components
*/
Vue.component('items-component', ItemsComponent);
Vue.component('change-title-component', ChangeTitleComponent);
Vue.component('add-item-component', AddItemComponent);
new Vue({
el : '#app',
data: data
});
Index.html file
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Shopping List</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
<style>
.container {
width: 40%;
margin: 20px auto 0px auto;
}
.removed label {
text-decoration: line-through;
}
ul li {
list-style-type: none;
}
ul li span {
margin-left: 5em;
}
.footer {
font-size: 0.7em;
margin-top: 20vh;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app" class="container">
<h2>{{ title }}</h2>
<add-item-component></add-item-component>
<items-component></items-component>
<div class="footer">
<hr />
<em>Change the title of your shopping list here</em>
<change-title-component></change-title-component>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-2.2.4.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.6/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.0.3/vue.js"></script>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Directives and Custom Directives
Enhance application behaviour.
v-model, v-if, v-show
Functions: bind, update and unbind
Vue.directive('my.directive', {
/**
* Do preparation for element binding
*/
bind: function() {
},
/**
* Do something based on the updated value
*/
update: function(newValue, oldValue) {
},
/**
* Do clean-up work
*/
unbind: function() {
}
});
In case of only update, the simplifyed way is:
Vue.directive('my-directive', function(el, binding){
/**
* Do something with binding value
*/
});
A custom directive v-square:
html file:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Vue Custom Directive Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input v-model="item" type="text" />
<div v-square="item"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.0.3/vue.js"></script>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
script file:
Vue.directive('square', function(el, binding) {
/**
* Do something with binding value
*/
el.innerHTML = Math.pow(binding.value, 2);
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {item: 42}
});
Plugins and Custom Plugins
Provides a rich set of functionality
Types:
- Add some global property or method: vue-element
- Add global assets: vue-touch
- Add vue instance methods to attach them to prototype
- Provide external functionality: vue-router
Plugin must provide an install method that has access to the global Vue object to modify and access it.
// VueMathPlugin.js
export default {
install: function(Vue) {
Vue.directive('square', function(el, binding) {
el.innerHTML = Math.pow(binding.value, 2);
});
Vue.directive('sqrt', function(el, binding) {
el.innerHTML = Math.sqrt(binding.value);
});
}
}
In order to use it, Vue.use(SomePlugin).
// script.js
import Vue from 'vue/dist/vue.js';
import VueMathPlugin from './VueMathPlugin.js';
Vue.use(VueMathPlugin);
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: { item: 49 }
});
Example:
Have the following files in order to have a custom plugin able to plug into vue application.
index.html, package.json, script.js, VueMathPlugin.js
VueMathPlugin.js is the main file which defines plugin behaviour.
script.js use the plugin to data binding
package.json is used to install the plugin using npm install and npm run build
{
"name": "vue-custom-plugin",
"scripts": {
"build": "browserify script.js -o main.js -t [babelify --presets [ es2015 ] ]"
},
"version": "0.0.1",
"devDependencies": {
"babel-preset-es2015": "^6.9.0",
"babelify": "^7.3.0",
"browserify": "^13.0.1",
"vue": "^2.0.3"
}
}
main.js is the generated file from: nom run build
index.html the main file which contains main.js
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Vue.js - Custom Plugin</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
<style>
#app {
width: 60%;
margin-top: 40px;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
input {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input v-model="item" />
<hr/>
<div><strong>Square:</strong><span v-square="item"></span></div>
<div><strong>Root:</strong><span v-sqrt="item"></span></div>
</div>
<script src="main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
When open index.html:
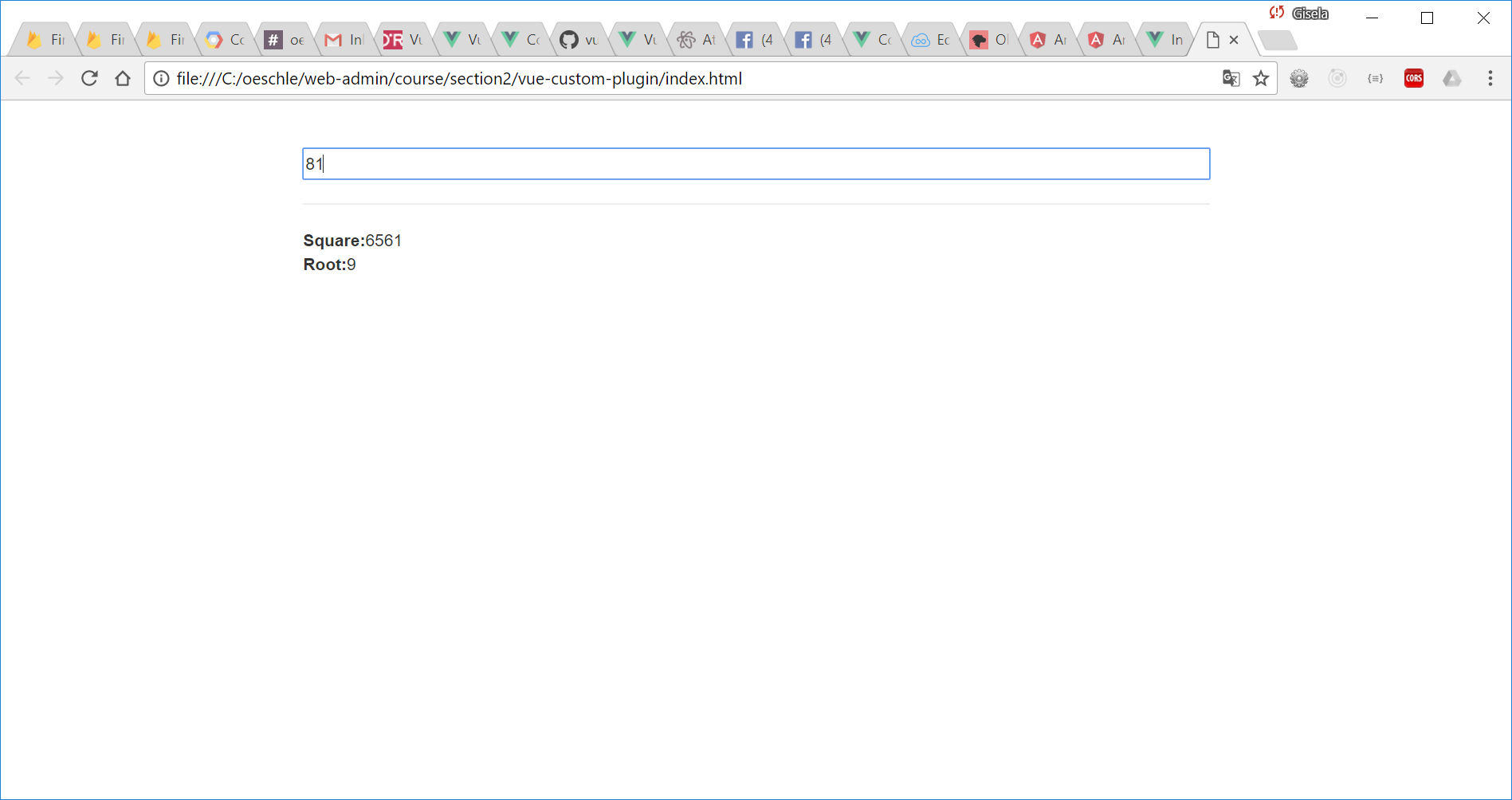
Application State and Vuex
When application becomes huge it is required to use a global store management.
https://facebook.github.io/flux/
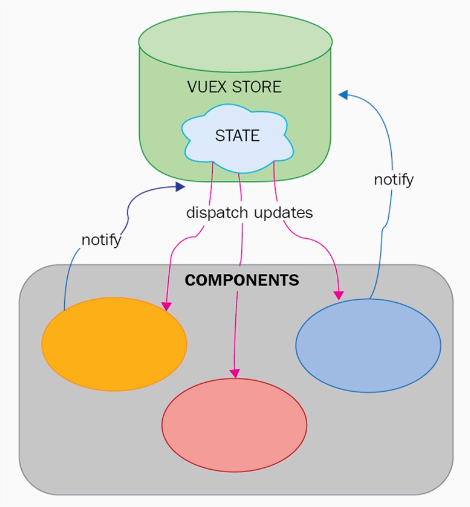
Once declared in the main component, the store could be use within the components:
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Vue from 'vue';
Vue.use(Vuex);
var store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
mutations: {}
});
new Vue({
components: components,
store: store
});
Vue-CLI
Allows initialization with different configurations:
- Webpack
- Browserify
- Simple
Installed with npm:
npm install -g vue-cli
Templating:
https://github.com/vuejs-templates
Initialize with webpack
Run:
vue init webpack
https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack
Initialize with simple
Run:
vue init simple vue-simple-config
Starting Complex SPA Project
Use webpack and browserify configuration