Searching History
Different ways to query Git to get useful information.
Reachability
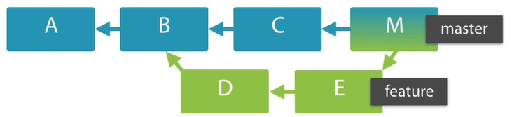
Each node (commit) could have more than one child (branching point or folk points), or to have more than one parent (merged commits).
Commit A is reachable from commit M if A is an ancestor of M.
Dot Dot notation
A way to query: which commits are in this branch but not in that other one?
Examples:
Which commit are reached from master head and not in feature head?
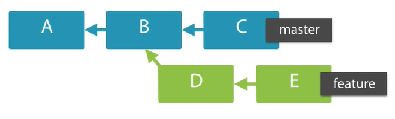
$ git log feature..master
Dot Dot Dot notation
This notation is unique to git log. It results in the commits that are reachable from either of the branches bot not from both.
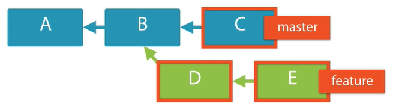
Examples:
git log feature...master
git log HEAD~2...5dfg565
Reachability of descendants
Using --ancestry-path
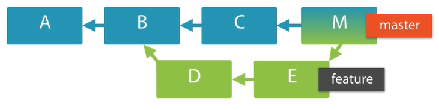
// The commits that are not only the ancestors of master but descendants of feature,
// It is M
git log --ancestry-path feature..master
Graph
git log master feature --graph
Show Branches
Shows a hierarchical view of the ancestry lines
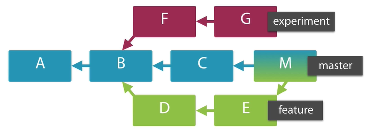
git show-branch feature master experiment
plus(+) regular commits
minus (-) merge commits
asterisc(*) reached by all the branches
PLEASE: use this command extensively
Tracking Commits
How to find the merged and not merged branches
// Find merged branches that is merged into the current one
$ git branch --merged
feature
* master
$ git branch --merged feature
feature
// Find not merged branches
$ git branch --no-merged
experiment
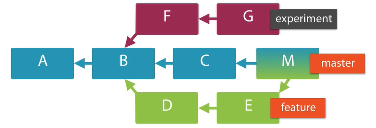
But tell me which commits.
$ git log HEAD..experiment
// with --topic to filter out the commits that have been merge into the first branch reference, showing only those
// which haven´t merged: this case is experiment branch
$ git show-branch --topic master feature experiment
Tell me what are the changes the commits introduced
Not all the time we introduce a whole commit but instead small pieces using cherry-picking for example. How to know which the changes are.
We want lo took for commits that are patch equivalent meaning they introduce the same set of changes as other commit regardless of the commit id.
In order to find them:
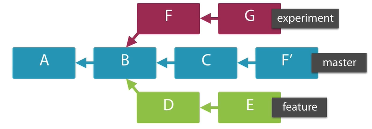
Next example: Finds the commits reachable from one branch whose patch is present in a commit that is reachable from another one and vice versa.
$ git log --cherry-mark --left-right --no-merges master...experiment
Results: the commits that are missing in the right side (experiment) are marked by a less than sign (<).
--left-right tell us: the ones missing on the left side (master) are marked with a greater than sign (>).
--left-only or --right-only already exist to filter only the side that is interested in.
The ones that are equal are marked with (=)
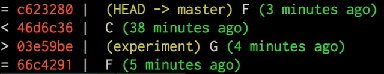
Next example: to find the commits that are not equivalent using --cherry-pick. Which commits are in one branch and not the other
$ git log --cherry-pick --left-right --no-merges master...experiment
// Know which commits are missing in master
$ git log --cherry-pick --right-only --no-merges master..experiment
// Shorthand version of: git log --cherry-mark --right-only --no-merges
$ git log --cherry master...experiment
// Shorthand version of which commits are missing in master
$ git log --cherry experiment...master
Know when a feature branch was merged into a master
That is, the list of merged commits that have happened between feature and master.
For example: all the merge commits that are reachable from master but not from feature
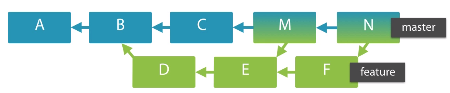
$ git log --merges feature..master
N and M
$ git log --merges --ancestry-path feature..master
N
//
$ git log --merges master--feature
empty because master never merges to feature
Tracking Changes
To track the changes across commits.
Commits associated to a file
Finds the commits which snapshots contain the file.
// Find commits id
$ git log --follow calculation.c
// Also know the specific changes in code
$ git log --follow --patch calculation.c
Commits which files contains a String
-S option only used to find in lines Added or Removed BUT not BOTH (that is ~modified).
-G option is used to include also the modified lines
// calculator is the string to find
$ git log -Scalculator
// using regular expressions
$ git log -S".*is.*" --pickaxe-regex
// to find also in modified lines
$ git log -Gcalculator
// to see the patch (code modified)
$ git log -Gcalculator --stat
// using regex is implicit with -G
$ git log -G"*.is.*"
Commits which files contains functions
Using language-aware diff.
// With L option seach for a function called substract in calculator.c file
$ git log -L:substract:calculator.c
Language Parcels: Git is able to recognize C and C++ languages out of the box. We can use other language in order to Git identifies. It is necessary to tel Git which language parcel to use in which files (Java for example) .
Add an entry in .gitattributes.file:
// Entry in the file seems that:
*.java diff:java
http://bit.ly/git_language_parsers
Tracking Authors
Who authored the patch? Person who did the code
Who commit into repository? Person who commit the code
Examples:
$ git log --author="Gisela Medina"
Search info for last commit give us author and commiter info:
$ git log -1 --pretty=fuller
Search all commits done by a specific committer:
$ git log --committer="Gisela Medina"
Search all commits done by an author:
$ git log --author="Gisela Medina" --since="1 week"
$ git log --author="Gisela Medina" --since="1 week" --until="2 days ago"
See to dates: https://git.io/approxidate
Search for changes done by author by lines of code
Find the authorship in a file:
$ git blame calculator.c
// changes done in feature branch only
$ git blame master..feature calculator.c
// range by lines
$ git blame calculator.c -L14,16
// range by function name
$ git blame calculator.c -L:substract
Search for changes but simple way
// with -s total of commits per author
// with -n shows the result by that number
$ git shortlog -s -n | head 10